Hearing loss is a significant health concern in Singapore, a country with a rapidly ageing population.
A substantial percentage of older adults in Singapore suffer from some degree of hearing loss, with estimates suggesting that around 422,000 older adults are affected, and more than 100,000 may have a disabling hearing impairment.
The prevalence of such impairments is expected to increase, potentially doubling by 2030. Disabling hearing loss is considered significant enough to interfere with daily communication, where individuals may struggle to understand more than half of a conversation without visual aids.
These patients undergo a full clinical evaluation by otorhinolaryngologists (ENT surgeons) and audiologists. An audiogram (hearing test) is conducted to measure one’s ability to pick up sounds of different frequencies (pitch). No further testing is required unless specific abnormalities are detected.
What causes hearing loss?
Hearing loss can be caused by various factors. Some of them include:
- Cerumen impaction (impacted ear wax)
- Trauma to the ear or head
- Loud noise / loud sounds
- Ototoxic medicines
- Work-related ototoxic chemicals
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Viral infections and other ear conditions
- Delayed onset or progressive genetic hearing loss
- Sudden sensorineural hearing loss
Types of hearing loss
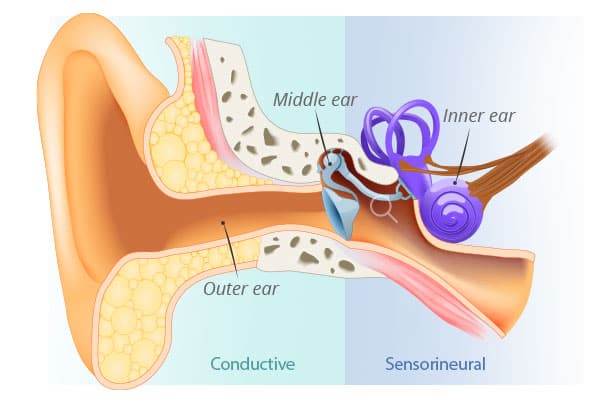
Conductive hearing loss
Occurs when there is a problem with the ear canal, eardrum, or middle ear that prevents sound waves from reaching the inner ear.
Causes: Ear infections, earwax blockage, fluid in the middle ear, perforated eardrum, or abnormalities in the ear's structure.
Sensorineural hearing loss
This results from damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or the auditory nerve, disrupting the transmission of signals to the brain.
Causes: Ageing, exposure to loud noises, certain medications, genetics, head trauma, or illnesses that affect the inner ear.
Mixed hearing loss
Combination of both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, indicating problems in both the outer / middle ear and the inner ear or auditory nerve.
Causes: Typically a combination of factors leading to issues in both the conductive and sensorineural components of hearing.
Impact of hearing loss
Hearing loss impairs a person’s ability to communicate and appreciate pleasurable sounds like music. Leaving it untreated can lead to social isolation, anxiety, and even depression. The ability to hear also affects personal safety as everyday routines such as crossing the road or warning alarms.
When unaddressed, hearing loss can impact many aspects of life at an individual level:
- Communication and speech
- Cognition
- Education and employment: In developing countries, children with hearing loss and deafness often do not receive schooling. Adults with hearing loss also have a much higher unemployment rate. Among those who are employed, a higher percentage of people with hearing loss are in the lower grades of employment compared with the general workforce.
- Social isolation, loneliness, and stigma

Preventing hearing loss
Many of the causes that lead to hearing loss can be avoided through early intervention. Most common causes of hearing loss in adults, such as exposure to loud sounds and ototoxic medicines, are preventable.
Effective strategies for reducing hearing loss at different stages of the life course include:
- Immunisation
- Good maternal and childcare practices
- Genetic counselling
- Identification and management of common ear conditions
- Occupational hearing conservation programmes for noise and chemical exposure
- Safe listening strategies for the reduction of exposure to loud sounds in recreational settings
Managing hearing loss
Managing hearing loss requires a holistic approach. This includes psychosocial support and public education to increase understanding and compassion towards those affected.
For children, early detection and effective rehabilitation can enable a significant percentage to integrate well into mainstream education. Infrastructure and societal support are crucial for both children and adults to facilitate their integration into society.
Once hearing loss is identified it is essential to address it as early as possible, and in an appropriate manner, to mitigate any adverse impact.
How To Choose The Right Hearing Aids
Choosing the right hearing aids either for yourself or your loved one can be challenging. There is no one-size-fits-all solution and with the vast options of hearing aids today, this decision can be daunting. Therefore, it is important to understand the process and have a qualified audiologist or hearing care professional to guide you.
Make An Appointment
Make an appointment or contact the ENT clinic to consult an ENT Specialist about your condition. To make an appointment, select "Specialist Appointment". Under Specialist Appointment Details, select "Ear, Nose & Throat".
Make an enquiry. We will get back to you within 3 working days. You can reach us at 6311 1229.
