What is otitis media?
Otitis media, commonly known as ear infection, is the infection of the middle ear. Ear infections can be due to bacteria or viral infections. They are often painful as there is inflammation or fluid build-up. Ear infections, if not treated, can damage the middle and inner ear.
Main divisions of the ear
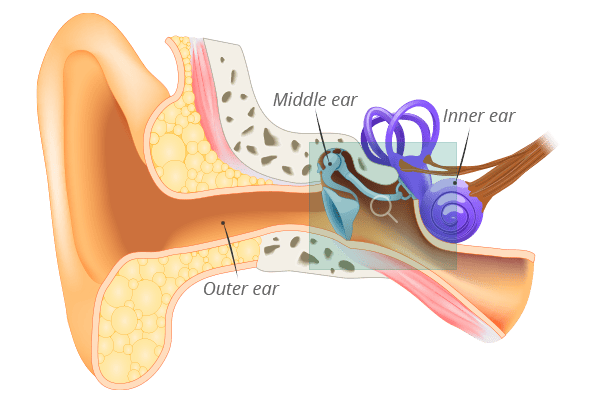
Healthy ear
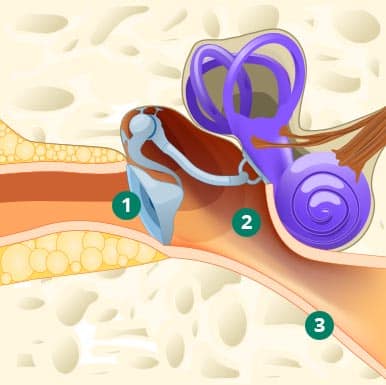
- Eardrum (tympanic membrane)
- Middle ear
- Eustachian tube
Ear infection
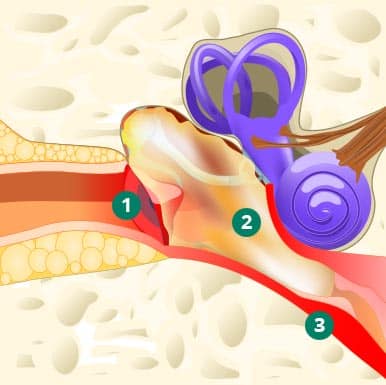
- Bulging, inflamed eardrum
- Thick mucous in middle ear
- Swollen eustachian tube
What are the types of ear infections?
Aside from common cold and other respiratory infection, which can result in ear infection, there are other types of ear infection that are caused by bacteria and viruses.
Middle ear infection
Ear infections are usually caused by bacteria like Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Haemophilus Influenza. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. The bacteria or virus will travel into the middle ear through the Eustachian tube, resulting in inflammation and build-up of fluid in the middle ear.
Fungal ear infection
Otomycosis, commonly known as ear fungal infection, is caused by the growth of fungus such as Aspergillus and Candida in the ear canal. Ear fungal infections are more likely to occur in warm and humid environment; hence the occurrence of fungal infection is common in tropical countries such as Singapore. They are also more common in people who swim, surf, or participate in water sports.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms vary for children and adult, however some common signs and symptoms can include:
- Pain in ears
- Loss of hearing
- Drainage from ears
- Difficulty sleeping
- Fever (more common in children)


Complications of ear infections
Ear infections that are not treated promptly can lead to serious complications.
Meningitis
Inflammation or infection of the tissues surrounding the brain and the spinal cord.
Mastoiditis
Inflammation of the mastoid bone (behind the ear).
Ruptured eardrum
The ear drum is responsible for sending sound waves into the inner ear. A damaged ear drum could result in the loss of hearing.
How are ear infections diagnosed?
The specialist will diagnose the condition of the ear with the use of a scope, to check the ear and the ear drum. Various tests will also be conducted to test the functionality of the ear.
Audiometry test (hearing test)
Audiometry is a hearing test that requires patient to sit in a soundproof room. Patient will wear a set of headphones that transmits specific sounds into one ear at a time. When the sound is heard, they will need to press a button to indicate that they can hear.
Tympanometry
Tympanometry is a test to check the pressure of the middle ear cavity to ensure that the middle ear is working well. A device with an earphone tip is placed in the ear and a small suction will be felt during the process.
What are the treatments for ear infections?
The specialist will prescribe eardrops, antibacterial, or antifungal cream to treat the inner ear canal depending on the severity and type of infection. In more severe cases, medication such as antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
How can I prevent ear infections?
Do not smoke and avoid second hand smoke
Smoking or inhaling second hand smoke increases the likelihood of ear infections.
Get recommended immunisation
Going for flu vaccines can help keep cold at bay and reduce the chances of catching a cold.
Dry your ears thoroughly after swimming
Fluid accumulated in the ear canal provides a good breeding ground for bacteria, resulting in the development of an infection.
Make An Appointment
Make an appointment or contact the ENT clinic to consult an ENT Specialist about your condition. To make an appointment, select "Specialist Appointment". Under Specialist Appointment Details, select "Ear, Nose & Throat".
Make an enquiry. We will get back to you within 3 working days. You can reach us at 6311 1229.
References
cdc.org - Ear infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Link)
my.clevelandclinic.org - Ear infection (otitis media): Symptoms, causes, prevention & treatment (Link)
healthline.com - Ear infection: Symptoms, causes, treatment, and more (Link)
mayoclinic.org - Ear infection (middle ear) (Link)