What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer develops within the cells in the skin. There are three main types of skin cancers. However, there are many other types derived from various parts of the skin.
The main types are:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma (Non-melanoma skin cancers)
- Malignant melanoma
Risk Factors in Developing Skin Cancers
1. Fair skin which burns easily

2. History of sunburns
3. Excessive UV light exposure
4. Multiple moles or unusual looking moles

5. Family history or personal history of skin cancers

6. Weakened immune system
Non-melanoma Skin Cancers
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) and Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) are by far the commonest skin cancers.
- They usually appear on sun-exposed skin, head and neck, scalp, limbs.
- BCCs usually present as a dome-shaped lesion with an ulcer on the surface, also known as nodular BCC / rodent- ulcer. However, BCCs can present very subtly as a scar-like lesion known as infiltrative BCC, or a scaly lesion known as superficial BCC.
- SCCs present as non-healing ulcerated scaly lesions.
- In early stages, these cancers may not be easily diagnosed. A skin biopsy may be recommended to determine the nature of the skin growths.
- These cancers are usually not metastatic and therefore do not commonly spread to other parts of the body / organs.
- SCC however, may spread to lymph nodes and can be fatal if left untreated for many years.
- It is still important to treat them early if detected.
- If left alone, they can grow larger and invade nearby tissues and organs, causing scarring, deformity, or even loss of function in some parts of the body.
- Your dermatologist will recommend treatment depending on the size, site involved, the extent of the tumour and your fitness for treatment. Ideally, they should be surgically removed.
Melanoma
- Melanomas are cancers which develop from the pigment cells in your skin called melanocytes. It is a serious form of skin cancer.
- Moles are benign / innocent growths from the melanocytes.
- Not all moles will evolve into cancer (melanoma), but any change to your moles require immediate attention by a dermatologist.
- Melanomas can occur anywhere on the body, but are more likely to start in certain areas, eg. the trunk (chest and back) in men and legs in women. The head and neck are other common places for melanoma to start.
- Fortunately, melanomas are not as common as basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers, but they can be far more serious.
- Melanoma can mostly be cured in its early stages. If left alone or ignored, melanoma is more likely to spread to other parts of the body, where it is more difficult to treat.
Skin Check
Self-examination and examination of your skin with help from a close family member would be advisable if you have multiple moles or risk factors for skin cancers.
Seek help from a dermatologist early if you or your family members detect:
- Skin sores that do not heal spontaneously
- Lesions that cause discomfort or tenderness
- Lesions that bleed
- Lesions that continue to grow in size
Observation is needed if a mole has the following suspicious features:
A: Asymmetry
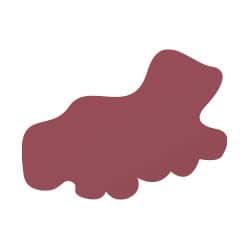
B: Borders (irregular, blurred)
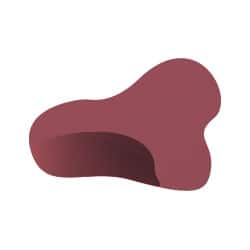
C: Colour (varying colours)
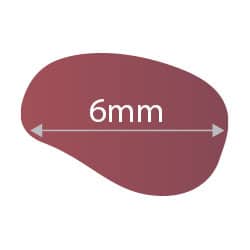
D: Diameter (more than 6mm)
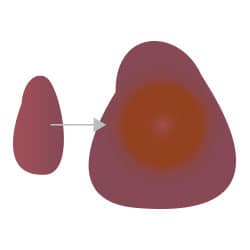
E: Evolution (changing over time)
Protection Against UV Rays
The catch phrase is Slip! Slop! Slap! and Wrap!:
- Slip on a shirt
- Slop on sunscreen. It is advisable to use sunscreens with at least SPF 30 and protection against UVA. Repeat application every four hourly
- Slap on a hat
- Wrap on sunglasses to protect the eyes and skin around them
In tropical weather, avoidance of direct sun during mid-day between 10am – 4pm is advisable.

Make An Appointment
Make an appointment online or contact a Raffles Skin & Aesthetics' clinic near you to consult a dermatologist. To make an appointment, select "Specialist Appointment". Under Specialist Appointment Details, select "Anti-ageing", "Dermatology".
Make an enquiry. We will get back to you within 2 working days. You can reach us at 6311 2340 or email us.
