What is atopic dermatitis (eczema) ?
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a common skin condition. It presents as itchy rashes on the skin. The onset is usually in infancy and childhood, but it may start later in adulthood as well.
Atopic dermatitis can affect any part of the body. During infancy, it frequently affects the face and outer areas of the arms and legs.
Later on, the typically affected areas are the neck and flexures. It is often associated with asthma and allergic rhinitis.
What is the cause?
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not fully understood. Alteration of the immune system and disruption of the skin’s barrier function and genes all play a part in the development of this condition. For some, factors that seem to worsen eczema include:
- Certain soaps, detergent, or chemicals
- Humidity or temperature changes
- Certain clothing materials like wool, etc
- Stress or emotional distress
Common eczema symptoms include:
- Red itchy rashes
- Dry skin
- Sensitive and/or inflamed skin
What are the treatments available?
It is important to determine what substances you are especially sensitive to so that you can focus on reducing your exposure to them.
If thought necessary, the dermatologist will recommend appropriate diagnostic and laboratory investigations in order to make the correct diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatments which may include:
Topical steroids – Effective in reducing skin inflammation, and is safe if used under a doctor’s supervision. Possible side effects include thinning of the skin, lightening of skin colour, and stretch marks.
Oral medication – In acute flares, short courses of oral antibiotics and/or steroids may be prescribed by your doctor. Oral antihistamines are frequently used, particularly at night, to reduce itching and scratching.
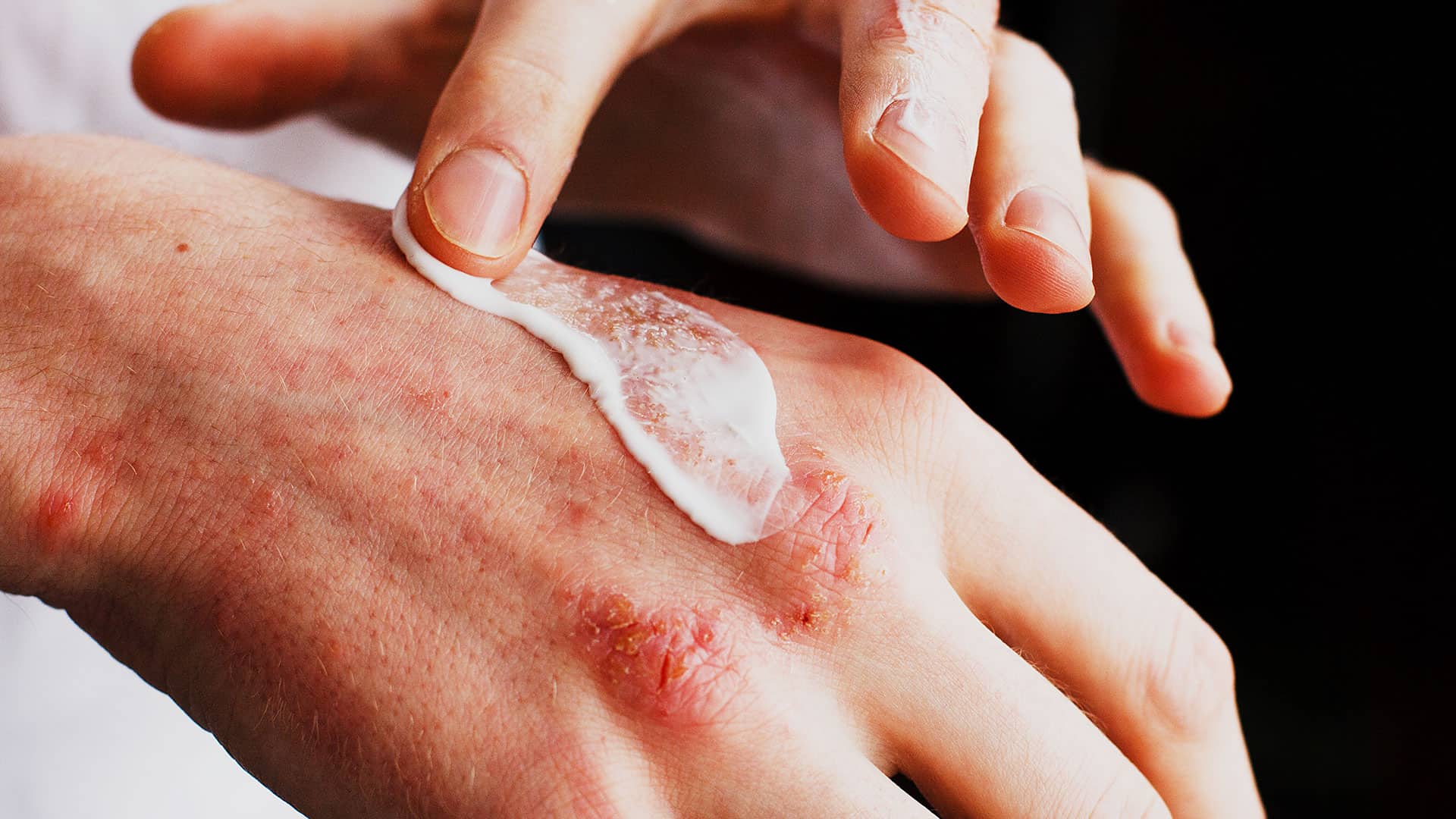
Moisturisers – They are important as dry skin is a key feature of atopic dermatitis.
Topical calcineurin inhibitors – Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus. These steriod-free topical agents are often used for delicate sites like the face and flexures.
Photo therapy / Immunosuppressive agents – In severe cases, ultraviolet light therapy or systemic immunomodulators like cyclosporin and azathioprine may be considered as a treatment.
Biologics (Dupilumab) – Also for severe cases, biologics work differently from other treatments. Instead of treating general inflammation, they target specific molecules causing atopic dermatitis, and are safer than immunosuppressive agents.
JAK inhibitors – This is the latest oral immunosuppressive agent which work quickly to ease symptoms in severe cases.
Can eczema be cured?
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition that tends to flare up periodically. In some cases, the skin condition may improve with age.
Living with eczema
- Skin care is important in people with atopic dermatitis. Gentle soaps or soap-free cleansers should be used for cleansing. Lukewarm or cool water should be used as hot water will strip the skin of its natural oils.
- Moisturisers should be applied liberally to the skin and the best time to do so is after a shower.
- Scratching should be avoided as it makes eczema worse. Physical activities should be minimised during flares as heat can also worsen the skin condition.
Make An Appointment
Make an appointment online or contact a Raffles Skin & Aesthetics clinic near you to consult a dermatologist. To make an appointment, select "Specialist Appointment". Under Specialist Appointment Details, select "Anti-ageing", "Dermatology".
Make an enquiry. We will get back to you within 2 working days. You can reach us at 6311 2340 or email us.
