6 Medical Tests To Diagnose Heart Problems

Did you know that your heart is one of the most powerful organs in the human body?
It consistently pumps blood throughout every beating moment of your life without fail. This process never stops and is occurring right now even as you are reading these words.
The heart is one of the organs whose activities are mostly unnoticed, yet, when a problem presents, its reactions are easily felt. It is therefore, imperative for doctors to identify what exactly is wrong once a symptom is experienced.
Apart from having a good family history and undergoing examination, here are some useful medical tests that specialists use to help diagnose what might be wrong with the heart.
Diagnostic Tests for the Heart
Diagnostic tests for the heart can be broadly classified into two categories – invasive and non-invasive. These tests are important as they help the doctor determine what is wrong with the heart. It can be an electrical problem where the heartbeat is too slow or too fast. Alternatively, it could also be a structural problem with the heart muscle, heart valves, or the heart’s blood supply.
By knowing what these tests involve and why they are being performed, it can help you feel more confident about them. This allows you and others to make an informed decision on which test to select.
Non-invasive Tests
The most common heart problem is the narrowing of the blood vessel. Non-invasive tests include exercise stress test, stress echocardiogram (ECG), or computerised tomography (CT) coronary angiogram, where we can accurately visualise the state of our coronary arteries.
For electrical problems, a basic ECG is usually conducted to see how the heart circuit is wired, while for patients with arrhythmia, there are devices for extensive monitoring of their heart rate for up to seven days. This can be done without requiring the patient to be hospitalised.
Invasive Tests
Invasive tests involve the insertion of catheters into the body. This can be done safely under local anaesthesia. While invasive in nature, these procedures are performed by specialists who are constantly monitoring you throughout the procedure.
These catheters help in identifying potential blockages in the blood vessel, and allows the narrowing to be treated simultaneously.
What is an Electrocardiogram (EKG / ECG) aka Electrocardiography?
An EKG / ECG records the electrical activity of the heart. This includes the timing and duration of each phase of the heartbeat.
Why this is done: An ECG provides two important information. Firstly, by measuring time intervals on the test, a doctor can find out how long it takes an electrical wave to pass through the heart. This information shows if the activity is too normal or slow, fast or irregular. Next, the test tells doctors if parts of the heart is too large or overworked. Sometimes, we can also learn if there is possible narrowing of patient’s blood vessel.
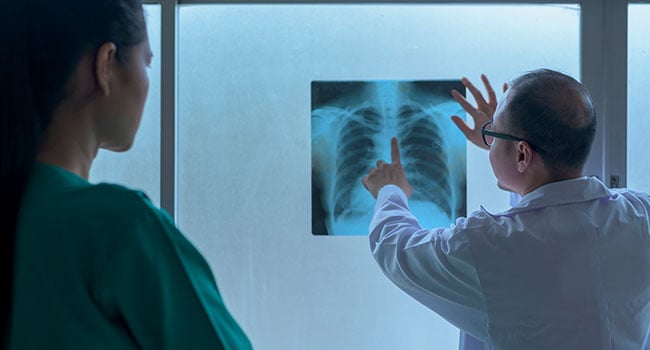
What does a Chest X-Ray show?
A chest X-ray is simply a picture of the chest. It shows the location, size, and shape of the heart, as well as its blood vessels.
How this is done: The patient’s chest will be placed next to the X-ray film and they will then be asked to hold their breaths and be still for two to three seconds. During this time, a beam of X-ray passes through the chest and an image is captured on a special photographic film.
What are Holter Monitors?
A Holter monitor is a battery-operated device that records your heart activity continuously for up to a week. It is a very small device attached to electrodes on your skin.
Why is this done: While an ECG test allows the doctor to look at the activity within the heart, results only reflect for activities recorded during that window. Abnormal heart symptoms may come and go unpredictably. Therefore, it may be required to monitor over time while the patient goes about their daily activities.
What are Cardiac Computed Tomography (CT) Scans?
Cardiac computed tomography (CT) scans are diagnostic imaging tests that are commonly done these days. They can determine the calcium score that tells us the extent of our cholesterol deposit in our heart arteries. By injecting contrast (also known as dye) into the bloodstream, we can also better visualise the heart structure and show any blockage that a patient may have in their coronary arteries.
Why this is done: Such scans are recommended in selected patients that present with chest pain, or have completed other tests and are suspected to have narrowing blood vessels. CT scans also provide additional information, like the amount of plaque build-up in a patient’s arteries.
What is an Electrophysiology (EP) Study?
An EP study is a detailed evaluation of the electrical activity in one’s heart. During an EP study, catheters inserted into the body are guided by a fluoroscopy machine into the heart. These catheters sense the electrical activity of the heart, and are able to stimulate increased heartbeats.
Why this is done: EP studies are usually recommended when other tests, such as Holter monitors, ECGs, or angiograms, are unable to provide enough information to thoroughly explain a patient’s abnormal heart rhythm. The test allows a safe reproduction of an abnormal heart rhythm. From here, specialists will then able to provide adequate medications that can best control it.
If the abnormal rhythm is a fast rhythm like atrial fibrillation or supraventricular tachycardia, specialists can then treat the condition with cardiac ablation, a minimally invasive procedure that treat the abnormal pathways responsible for arrhythmia.
What is a Transesophageal or Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TEE)?
A 2D ECG is a very useful and common test that is conducted using ultrasound waves to assess heart structures. The test is painless and it provides a myriad of information on the heart valves and cardiac chambers.
The TEE test also utilises ultrasound technology to provide a closer look at the heart’s valves and chambers. This is done by placing the ultrasound equipment on an endoscope – a thin and flexible instrument, and guiding it down the patient’s oesophagus. Once in position, pictures of the heart are obtained at various angles using ultrasound technology.
Why this is done: A TEE test is usually performed when a specialist needs to accurately assess the heart’s valves and chambers. A TEE allows for a closer look at the small and detailed structures of the heart as well as its associated vessels.




